PDF) Mycobacterium smegmatis whmD and its homologue Mycobacterium tuberculosis whiB2 are functionally equivalent

Potential Repurposed Drug Candidates for Tuberculosis Treatment: Progress and Update of Drugs Identified in Over a Decade | ACS Omega
Frontiers | Metabolic pathways that permit Mycobacterium avium subsp. hominissuis to transition to different environments encountered within the host during infection
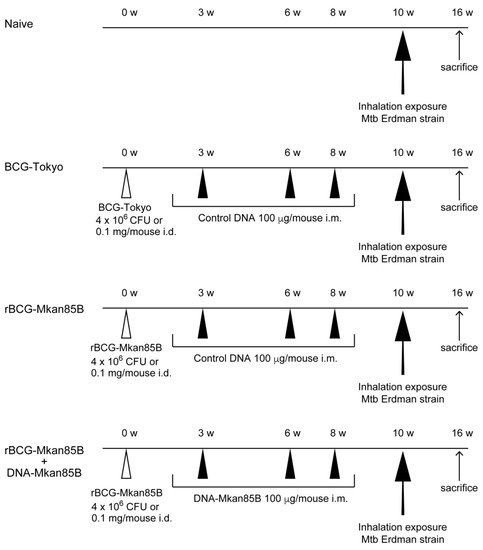
IJMS | Free Full-Text | The Induction of Antigen 85B-Specific CD8+ T Cells by Recombinant BCG Protects against Mycobacterial Infection in Mice
Biology | Free Full-Text | M.tb-Rv2462c of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Shows Chaperone-like Activity and Plays a Role in Stress Adaptation and Immunomodulation
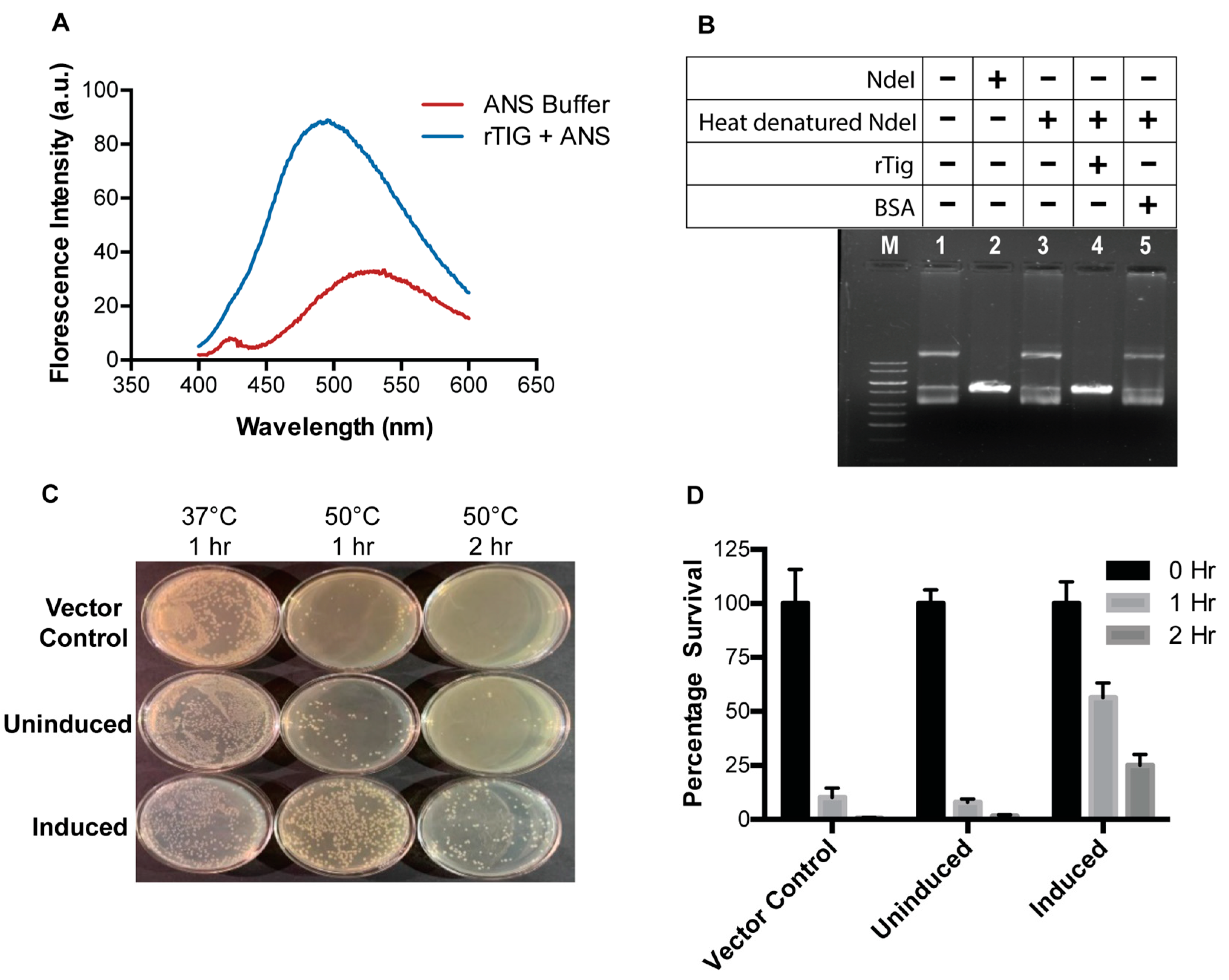
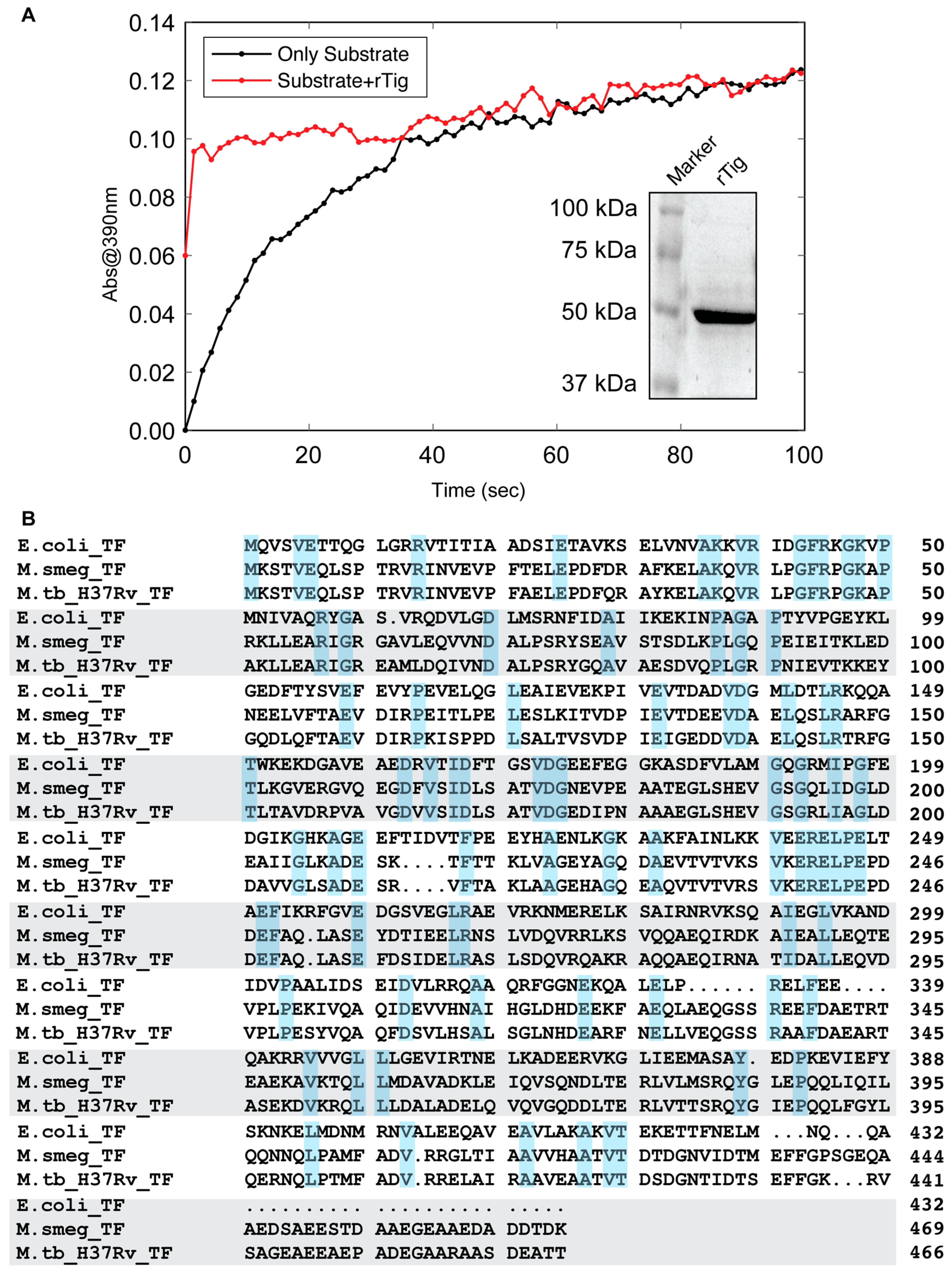
Biology | Free Full-Text | M.tb-Rv2462c of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Shows Chaperone-like Activity and Plays a Role in Stress Adaptation and Immunomodulation
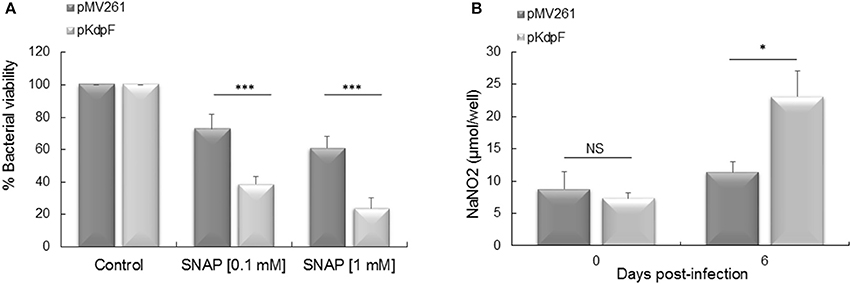
Frontiers | Endogenous and Exogenous KdpF Peptide Increases Susceptibility of Mycobacterium bovis BCG to Nitrosative Stress and Reduces Intramacrophage Replication

The Mycobacterium tuberculosis CRISPR-Associated Cas1 Involves Persistence and Tolerance to Anti-Tubercular Drugs

The Mycobacterium tuberculosis CRISPR-Associated Cas1 Involves Persistence and Tolerance to Anti-Tubercular Drugs

HDAC3 inhibitor RGFP966 controls bacterial growth and modulates macrophage signaling during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection - ScienceDirect

A) Map of the allelic exchange plasmid pAF102. The functional segment... | Download Scientific Diagram
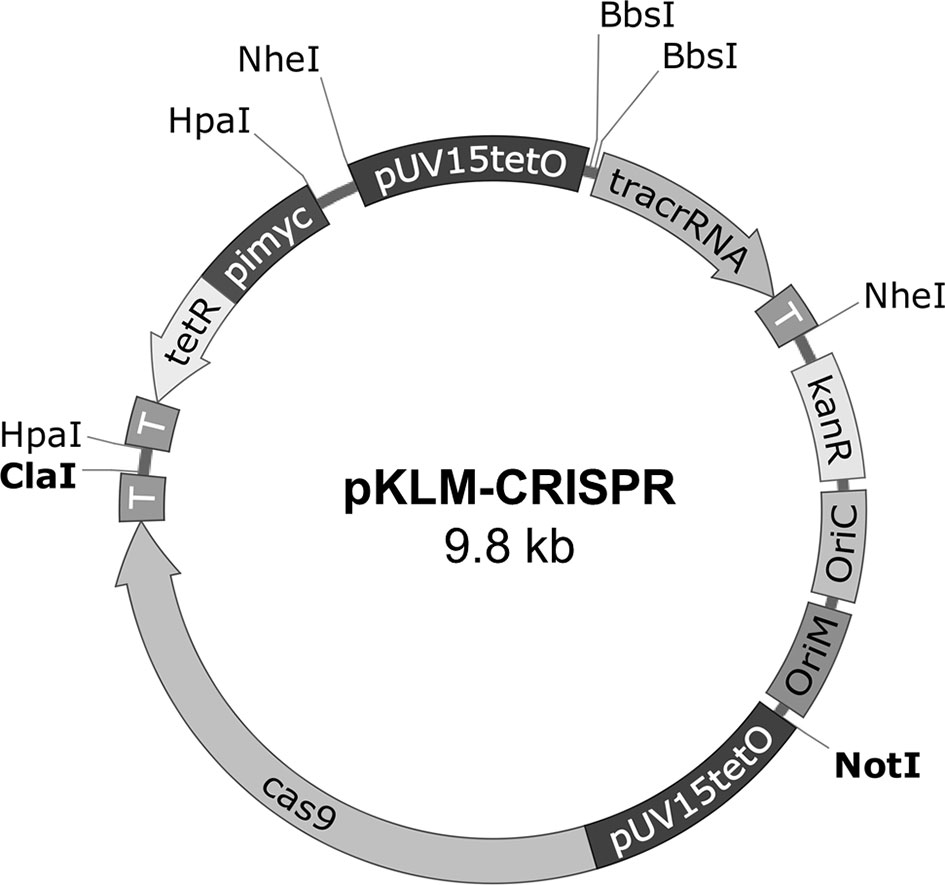
Frontiers | CRISPR/Cas9 Approach to Generate an Auxotrophic BCG Strain for Unmarked Expression of LTAK63 Adjuvant: A Tuberculosis Vaccine Candidate

Systematic Evaluation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Proteins for Antigenic Properties Identifies Rv1485 and Rv1705c as Potential Protective Subunit Vaccine Candidates | Infection and Immunity
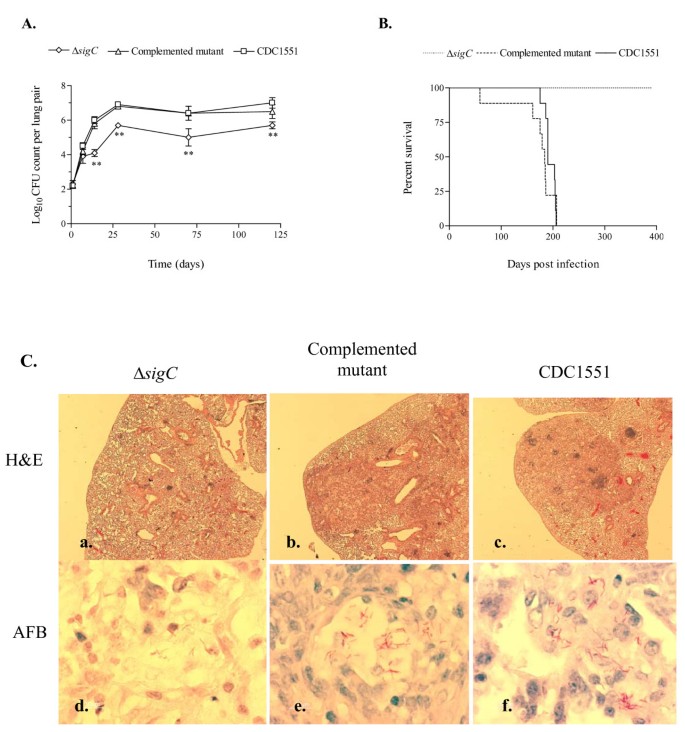
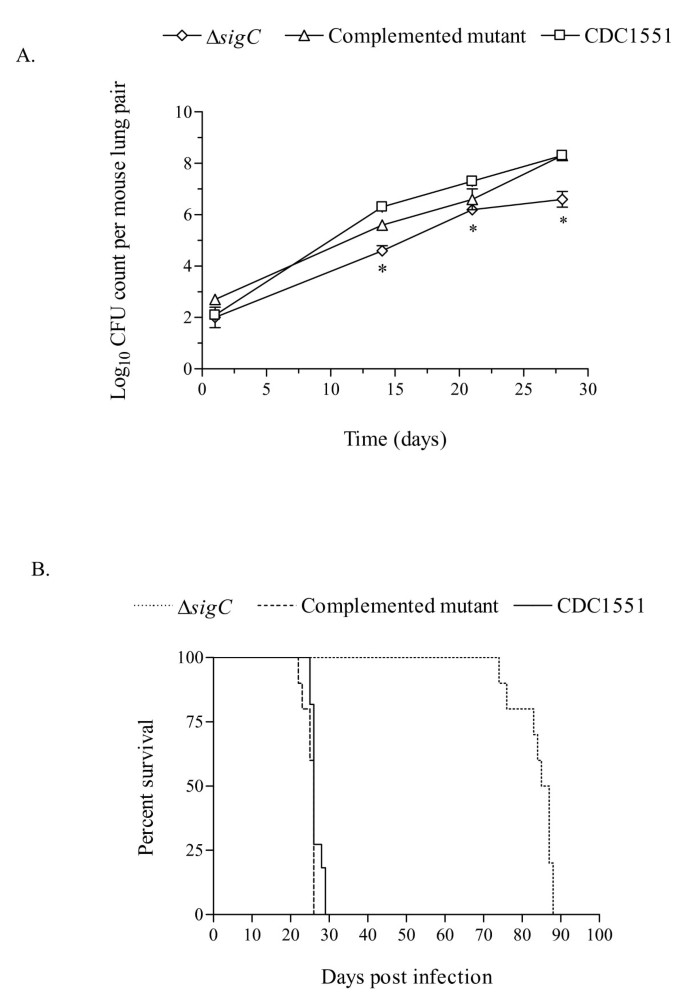
Altered cellular infiltration and cytokine levels during early Mycobacterium tuberculosis sigC mutant infection are associated with late-stage disease attenuation and milder immunopathology in mice | BMC Microbiology | Full Text

BCG‐mediated protection against M. tuberculosis is sustained post‐malaria infection independent of parasite virulence - Tangie - 2022 - Immunology - Wiley Online Library
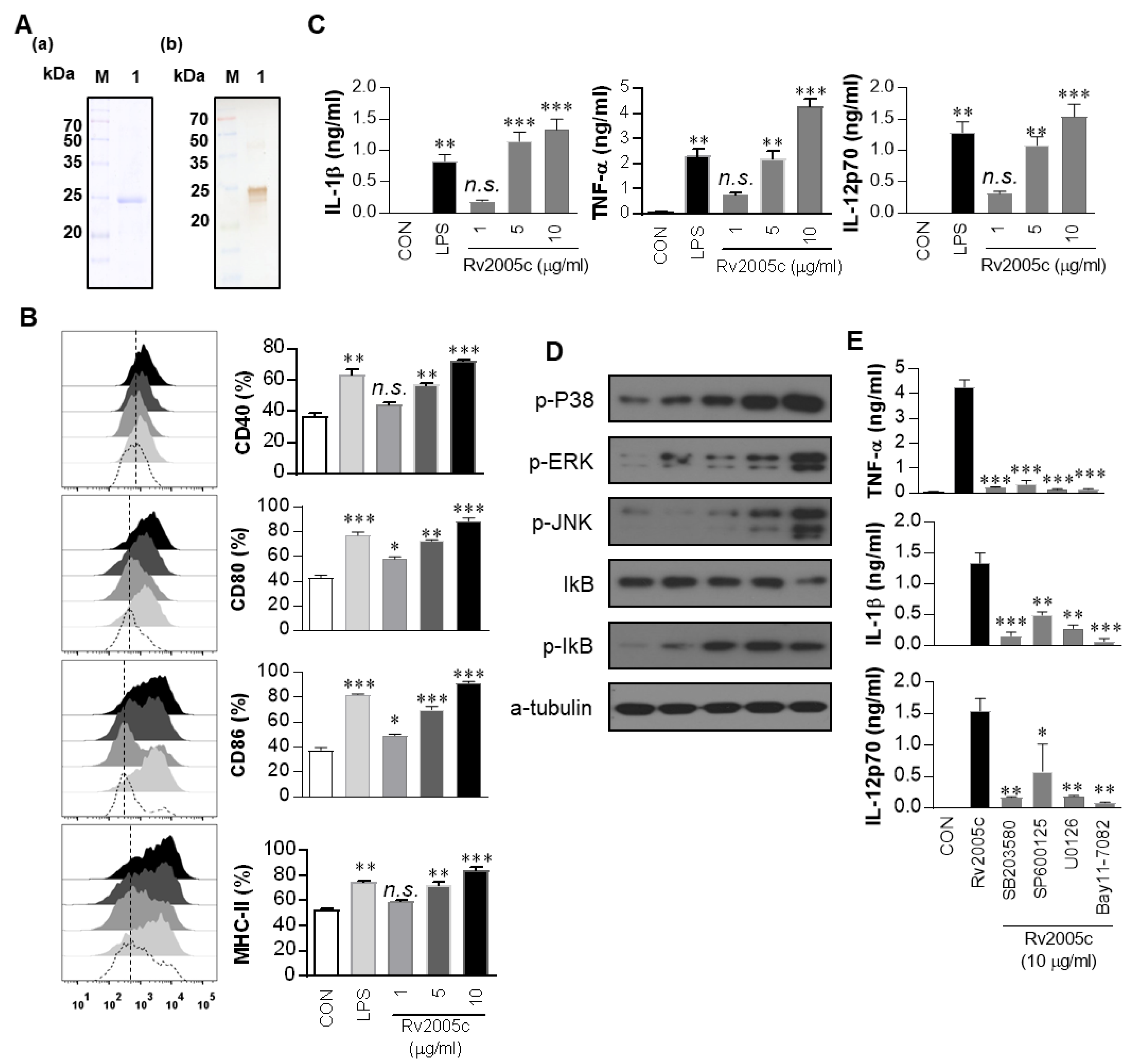
Vaccines | Free Full-Text | Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2005c Induces Dendritic Cell Maturation and Th1 Responses and Exhibits Immunotherapeutic Activity by Fusion with the Rv2882c Protein
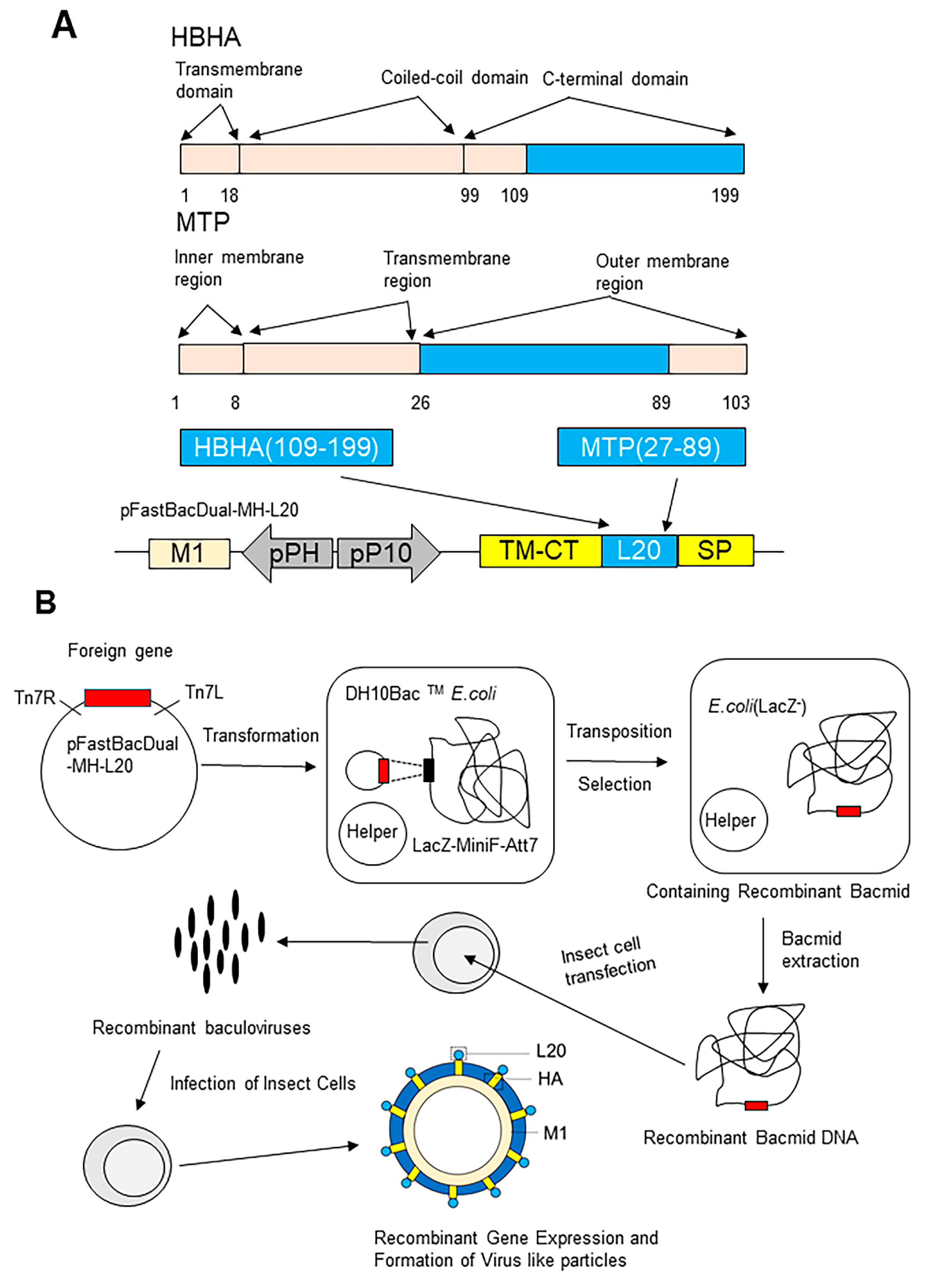
Vaccines | Free Full-Text | A VLP-Based Vaccine Displaying HBHA and MTP Antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Induces Potentially Protective Immune Responses in M. tuberculosis H37Ra Infected Mice
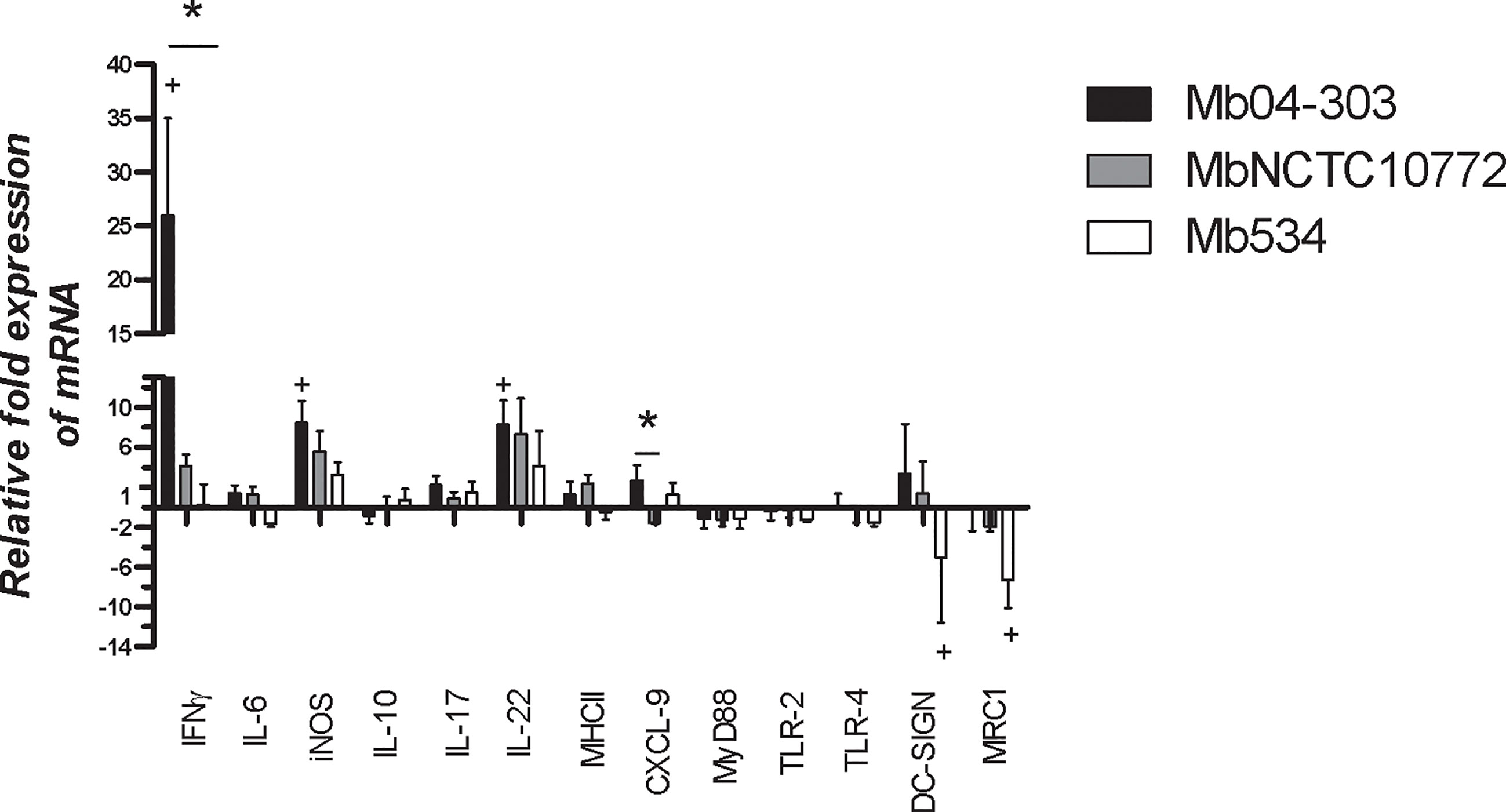
Frontiers | Identifying Bacterial and Host Factors Involved in the Interaction of Mycobacterium bovis with the Bovine Innate Immune Cells

Late stage specific Rv0109 (PE_PGRS1) protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces mitochondria mediated macrophage apoptosis - ScienceDirect

PPE38 Modulates the Innate Immune Response and Is Required for Mycobacterium marinum Virulence | Infection and Immunity

PPE38 Modulates the Innate Immune Response and Is Required for Mycobacterium marinum Virulence | Infection and Immunity

Mycobacterium tuberculosis PPE7 Enhances Intracellular Survival of Mycobacterium smegmatis and Manipulates Host Cell Cytokine Secretion Through Nuclear Factor Kappa B and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling | Journal of Interferon & Cytokine ...
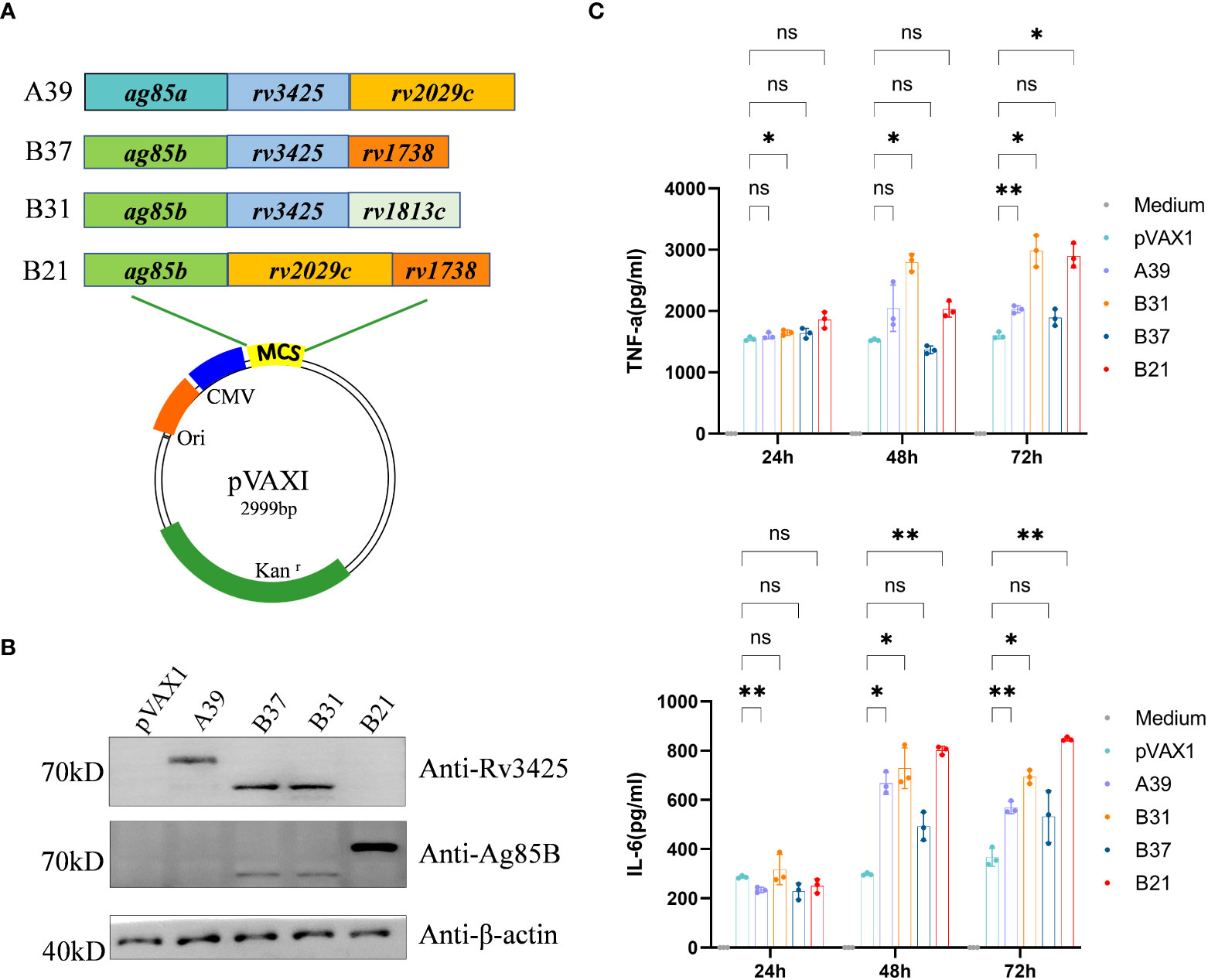
Frontiers | B21 DNA vaccine expressing ag85b, rv2029c, and rv1738 confers a robust therapeutic effect against latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection